Appearance
Introduction
Project management typically involves the following steps:
Initiation: Identifying and defining the project, its goals, and its stakeholders.
Planning: Developing a detailed plan for how the project will be executed, including schedules, budgets, and resource requirements.
Execution: Carrying out the project plan, including coordinating the efforts of team members and managing any changes to the plan.
Monitoring and controlling: Keeping track of progress, identifying and addressing any issues that arise, and making any necessary adjustments to the plan.
Closing: Completing the project and delivering the final product or service. This includes conducting a review of the project, documenting lessons learned, and closing out any remaining activities.
The goal of project management is to complete a project successfully, on time, within budget, and to the satisfaction of the stakeholders. Project managers use various tools, techniques, and methodologies, such as the project management triangle (also known as the triple constraint), to help ensure the project is a success.
Waterfall Methodology
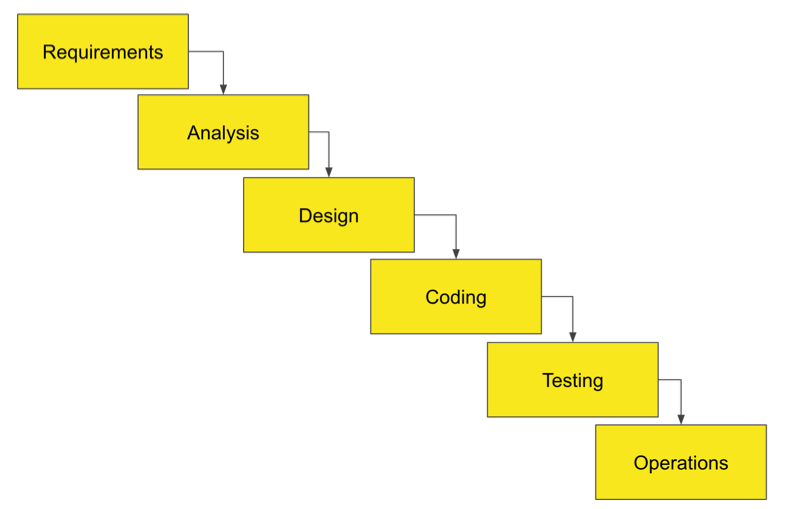
Waterfall project management is a traditional sequential approach to project management, where the project is seen as a cascading series of tasks that flow downwards, like a waterfall. In the Waterfall model, each stage of the project must be completed before the next stage can begin and progress is seen as flowing steadily downwards through the phases of Conception, Requirements, Analysis, Design, Coding, Testing, and Operations. The key characteristic of the Waterfall model is that there is no overlapping of phases, and each phase must be completed in its entirety before the next phase begins.
The Waterfall model is often used for projects with well-defined deliverables, a clear end goal, and where the requirements are understood and fixed. It's particularly useful in situations where the scope of the project can be defined upfront, and change is not expected. However, in many projects, the requirements are not fully understood or change frequently, which can lead to difficulties in using the Waterfall model.